
How Bread is made...
Stand:
Wheat is an important and widespread cereal. It is classified in two
fundamental groups: tender wheat and hard wheat.
In Northern Italy, the sowing time is early in November, while in Southern Italy
it is in December. Harvesting or reaping takes place between June and July.
Modern harvesters are complex machines that cut the wheat, thresh it (removing
the wheat from the chaff), put the seeds into sacks, and pack the straw.
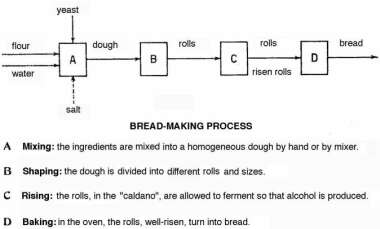
Bread is made of flour, water, and yeast, with or without the addition of
salt. Bread-making includes the following stages:
- mixing consists of combining flour, water, yeast and salt. The
yeast used in this process is constituted by micro-organisms (a kind of fungus)
which produce enzymes able to change chemically the dough during the process
of fermentation
- shaping consists of forming rolls which can have almost any shape
or size. They can be handmade or made by a machine
- rising is obtained by keeping the rolls for some time at a
temperature of 30°C; the fermentation takes place thanks to added
baking-powders. During this process the starch in contact with water
decomposes, in successive stages, into glucose, which, in its turn, ferments
changing into alcohol and carbon dioxide. This gas increases the volume of the
dough and makes it light and spongy
- during the baking process complex physical and chemical transformations
take place to give bread taste and digestibility. Oven temperature is kept at
around 220-270°C. Alcohol and carbon dioxide developed during the rising are
removed. Some water of the dough evaporates; the gluten coaugulates, outside a
crust is made and at last glucose candies
- once bread is baked, it is left to cool down in dry and ventilated rooms:
the loaf loses weight and becomes more crumbly and more digestible.
|



